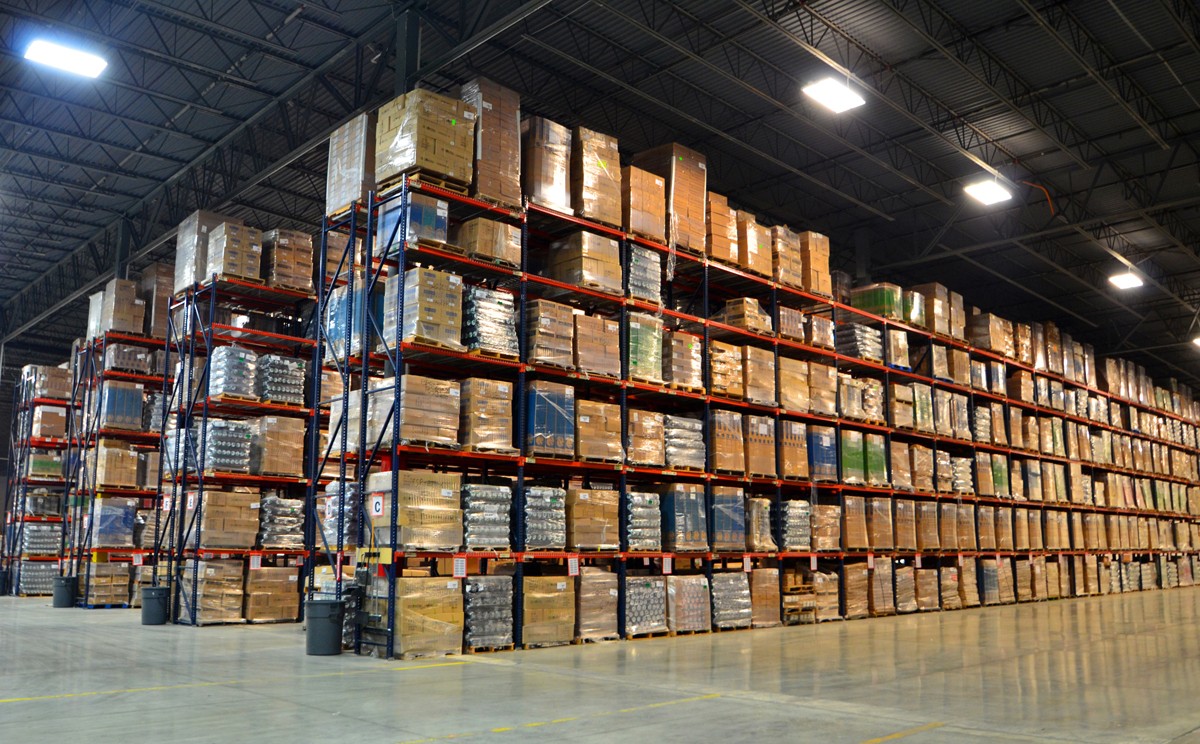
Warehouses will always remain an important component of the logistics system for any company. Having own warehouse is a necessity, rather than a whim, for those companies that are engaged in commercial activities or deal with goods. In any case, before building or leasing a warehouse, you need to understand what types of buildings are available and which one is suitable for your particular case.
What is a warehouse and its functions
A warehouse is a building, a plot of land or a combination of both, used for storing goods and providing a range of related services. Warehouses are used by retailers, wholesalers, logistics, transport companies, and other businesses in related areas. The warehouse is primarily intended to concentrate and preserve cargo stocks and to ensure prompt fulfilment of customer orders. The list of key warehouse functions is as follows:
- reformatting material flows;
- storage of cargo;
- reducing transportation costs;
- warehousing services;
- unloading of goods;
- loading of goods;
- acceptance of goods and quality assessment;
- packaging and labelling of goods.
What are the types of warehouses
The most common methodology for classification of warehouses has been developed by the Knight Frank brokerage agency. According to it, basic types of warehouses are:
- Class A+. A real luxury among all types of warehouses. The facility is being constructed specially for warehouse logistics needs. The warehouse is built on site with a convenient traffic interchange. The floor is additionally concreted to prevent wear and tear as a result of cargo turnover. The ceiling height must be at least 13 m.
- Class А. The organisational characteristics of Class A warehouses are almost identical to those of Class A+. They differ in ceiling height, which should be at least 10 m for warehouses of this category.
- Class B+. This category also includes those premises that were not constructed specifically for logistics needs, but were renovated for them. The ceiling height must be at least 8 m, which requires careful selection of equipment.
- Class B. This category consists exclusively of old buildings that have been renovated for logistics needs. They often consist of several floors, which makes it necessary to equip the premises with freight lifts. The minimum ceiling height is 6 m.
- Class C. This category includes buildings that were not originally used as warehouses. They are converted from workshops or hangars. The minimum ceiling height is 4 m.
- Class D. This type of buildings is generally not adapted for warehousing needs. This also includes former hangars and workshops. Modernisation and installation of special equipment for manual regulation of cargo storage conditions is impractical in this case. As a result, class D warehouses are only suitable for storing goods that do not require special storage conditions.
How to choose a warehouse
The choice of a particular warehouse depends on many factors, including the specifics of the company’s operations. For example, A and A+ warehouses can be used for storing highly sensitive electronics and medicinal products, while B and B+ warehouses are suitable for storing food and machinery. C warehouses are suitable for non-food products, and D warehouses can be used for short-duration storage of agricultural products, textiles or spare parts.
 EN
EN